 |
 |
The problem of forest fires is a major issue in the Mediterranean region. Rainfall occurring shortly after a fire can cause significant damage in terms of runoff volumes and material transport. In recent years, regional increases in temperature, aridity and drought have increased the frequency and intensity of fires, with a spatial extension beyond the regions previously commonly affected. The phenomena of runoff and soil erosion after a fire are not well known and decision-makers wish to identify the most effective actions to be implemented after fires.
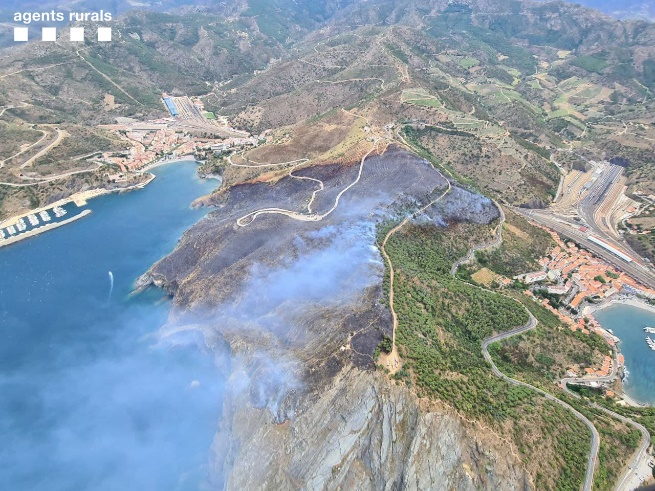
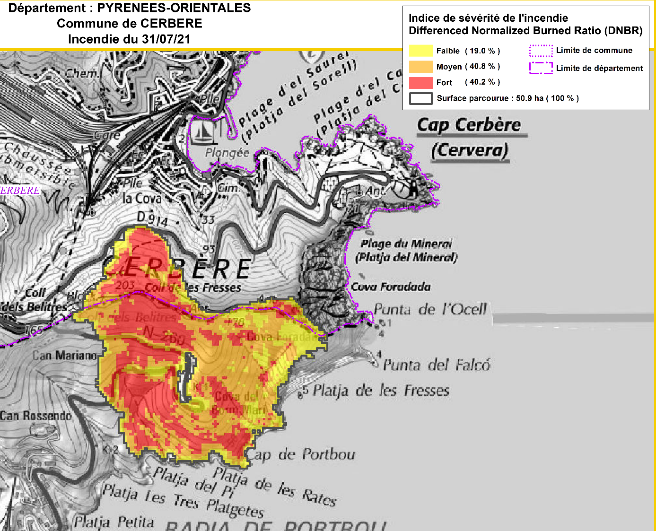
An initial assesment was conducted by ONF RTM on the the impact of fires on forest vegetation and its consequences on erosion and torrential hazard, then carried out an initial feedback on the impact of the Monze fire (Aude department) on 14 August 2019. In a second phase, instrumentation was installed on several key sites in the municipality of Cerbère (Pyrénées Orientales department), which suffered the passage of a 50 ha fire on 31 July 2021.

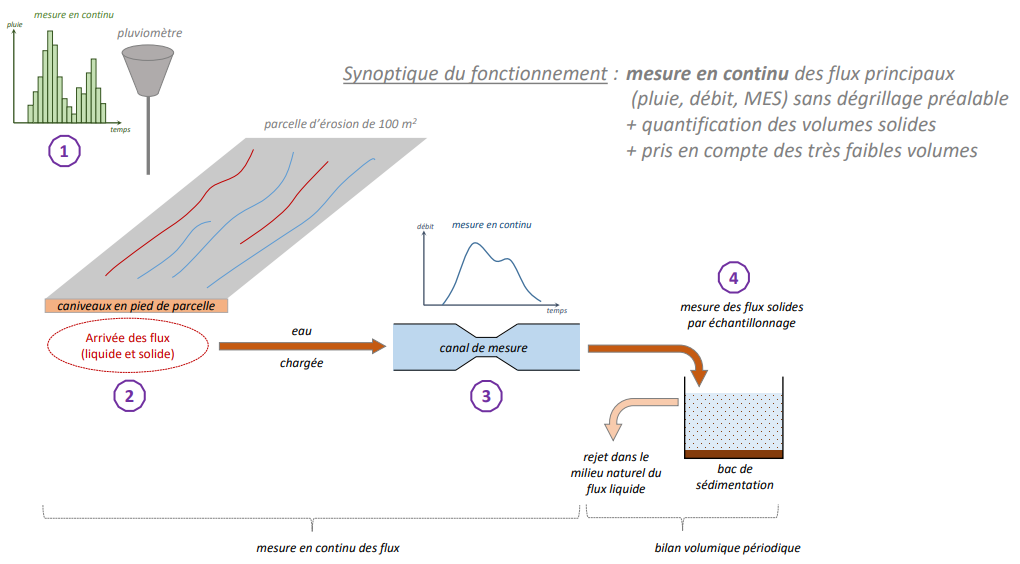
To better understand the mechanisms of soil water erosion, ONF RTM installed three expermiental plots in septembre 2021. The instaled instrumentation allowed the monitoring of rainfalls events during an hydrological season, measurements of rainfall, flow rate, watter height and sedmient quantities were taken. Thanks to the actions carried out in this pilot case (bibliographoc phase, the Monze fire feedback study and the instrumentation of the brurned plots in Cerbère), ONF RTM has further deepened the definition of the guidelines necessary to improve the mitigation of the torrentieal risk induced by the occurrences of forest fires.












